Legacy Maemo 5 Documentation/Human Interface Guidelines/Windows
Contents |
Windows
The concept of windows in Hildon is considerably different when compared to windows in a traditional desktop application. In Hildon, the organization of windows, as well as the parts that compose them, and their behavior change a lot. For instance, users cannot drag a window and move it around, since application windows in Hildon are fully maximized and the position of dialogs is fixed.
This section covers these differences by describing some of the windows' properties as well as how to organize windows and use particular types of windows (like wizard dialogs).
Window Views
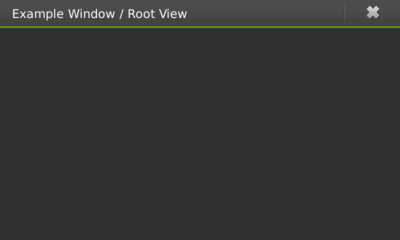
The concept of window organization changes in Hildon. On a traditional desktop application, it is normal that an action performed over an element in a window might bring up another window which can bring up a third one, and so on. On Hildon, the concept of window views is introduced. The idea behind window views is that windows are actually stacked and the user can only see the topmost one. An application can have several windows describing main tasks which are called root views (figure 1) and, on top of which, subviews (figure 2) are created. Whenever a subview is closed, the user is presented with the previous view. For instance, a root view could contain a list of email messages; selecting one of them would bring a subview displaying it.
Figure 1: A root window
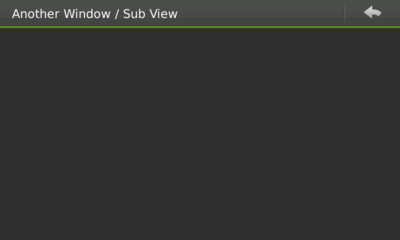
Many activities in an application should be presented and done in a subview and, after the user is done interacting with it, he or she can press the back button to go back to the previous view.
Figure 2: A sub view
Hence, split or tree views shouldn't be used. Instead, each area that could be split should be added to a window in the window stack. Consider as an example an email application. The root view would present the user with a list of options he can choose like ``Inbox, ``Outbox, ``Drafts, etc. If the user chooses ``Inbox, a new window is presented with the list of messages in the email's inbox. Clicking on a message from the list would bring in a new window with that message's content.
Note that it is important to choose when an action on an element in a window of a stack will either initialize a new subview or a fully independent window. Normally, new tasks that cut with the flow of actions are likely to mean a new independent window and not a new subview. For example, when browsing a to-do list, the action of creating a new to-do item should be a subview and not an individual window.
Properties of Windows
Titles
Every window should have a title. Although, given the small screen dimensions, a window title should neither be long nor contain unnecessary information. For example, do not include the program's version number in the title text.
Since only one window is shown at a time, it is quite easy for users to identify which application a visible window belongs to. Because of this, repeating an application's name in every window title is not required. In fact, doing so could even make the user's experience more complicated than it needs to be.
Sizes
When applications are in normal mode (not in full-screen mode), its main window should always occupy the maximum allowable size (i.e., the same size as the desktop, minus the top of the screen, where framework-specific information is displayed).
Window Modes
An application's window can either be displayed in normal or full-screen mode depending on application type and availability of modes.