Mer/Build/UsingGitorious
(added category) |
(Add verify step) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Moving a Package to Gitorious == | == Moving a Package to Gitorious == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Initial setup === | ||
| + | |||
The following scripts need: | The following scripts need: | ||
PKG=<package name> | PKG=<package name> | ||
| Line 64: | Line 67: | ||
git add debian/ | git add debian/ | ||
git commit -am "initial debianize from upstream" | git commit -am "initial debianize from upstream" | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Feature/patch branches === | ||
Now apply features from the .diff.gz | Now apply features from the .diff.gz | ||
this has to be done manually | this has to be done manually | ||
| - | |||
Identify a libtool feature | Identify a libtool feature | ||
| Line 108: | Line 112: | ||
git tag Mer_$TAG | git tag Mer_$TAG | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Verify === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remove all obs code: | ||
| + | cd .. | ||
| + | rm $PKG* | ||
| + | |||
| + | regenerate it: | ||
| + | cd $PKG | ||
| + | pristine-tar checkout ../$TARBALL | ||
| + | debuild -S -i.git | ||
| + | |||
| + | Build or examine to verify | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Push === | ||
Now push to gitorious | Now push to gitorious | ||
| Line 118: | Line 137: | ||
| - | Working from Gitorious | + | == Handling new upstream == |
| + | |||
| + | tba | ||
| + | |||
| + | nb push --tags | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Working from Gitorious == | ||
| + | This should be written to say "Clone this repository on gitorious" and then publish back there and then submit a pull request to Mer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For core work: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Essentially | ||
git clone git@gitorious.org:mer/$GPKG.git | git clone git@gitorious.org:mer/$GPKG.git | ||
git checkout --track origin/Mer | git checkout --track origin/Mer | ||
| + | |||
| + | determine which feature or branch needs work. Then: | ||
| + | git checkout --track origin/mer/<feature> | ||
| + | |||
| + | hack... | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ready to test? You need to make a local test branch based on Mer | ||
| + | git checkout Mer | ||
| + | git checkout -b local | ||
| + | git merge mer/<feature> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Build and test... | ||
| + | |||
| + | If this works OK then clean up your mer/<feature> branch... probably doing a <code>--squash</code> and push the branch to gitorious. | ||
[[Category:Mer]] | [[Category:Mer]] | ||
Revision as of 13:28, 17 June 2009
Contents |
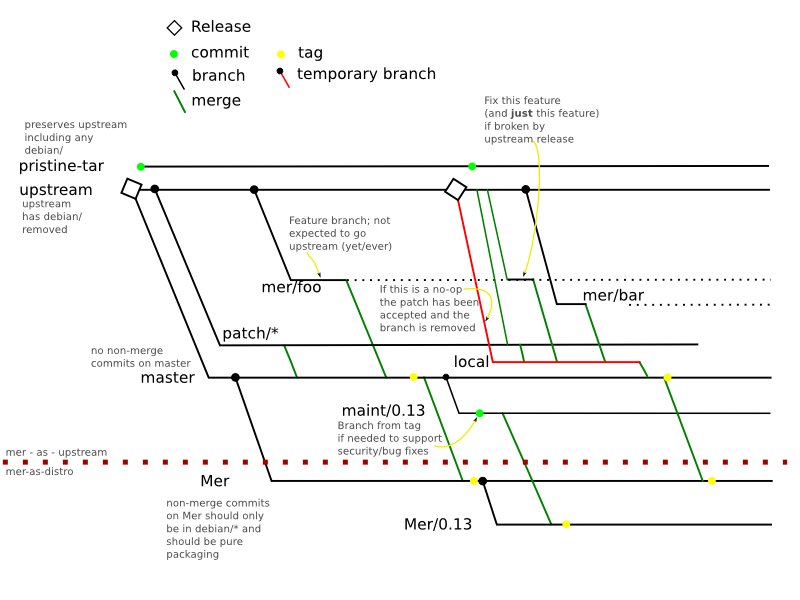
Packaging
The Mer DVCS packaging process looks like this:
An upstream package is unpacked and the debian/ directory is removed.
It is then commited onto the upstream branch.
pristine-tar is used to ensure that the upstream tarball can be recreated perfectly.
master is the main branch and the only non-merge commits directly on this branch should be packaging-based and in debian/
All features or bug fixes are broken out to additional branches; 1 branch per feature or fix. The main difference is that features are not likely to go upstream whilst fixes are. This is very similar to quilt.
Developing
Development of a feature is done by cloning master; then branching locally and developing against master.
Once development is complete a new feature branch is created and the development branch is then cherry-picked onto the new feature branch.
Moving a Package to Gitorious
Initial setup
The following scripts need:
PKG=<package name> GPKG=<gitorious-safe package name> (ie [a-z0-9_-] UPVER=<upstream version> TARBALL=<tarball name> TAG=<new version>
Get the upstream source unpacked
mkdir $PKG cd $PKG mkdir _tmp cd _tmp tar xf ../../$TARBALL mv */* ../ cd .. rm -rf _tmp
Cleanse the install
mv debian ..
Create a git repo with the new stuff
git init
git add .
git commit -am"${PKG}_$UPVER"
This is really the upstream branch
git branch -m master upstream
For keeping an eye on things you may want gitk running. Use File->reload frequently (F5 doesn't work for me)
gitk --all &
Save state
pristine-tar commit ../$TARBALL
Prepare structure create master branch from upstream
git checkout -b master
create Mer branch from master
git checkout -b Mer
Apply debianisation
mv ../debian . git add debian/ git commit -am "initial debianize from upstream"
Feature/patch branches
Now apply features from the .diff.gz this has to be done manually
Identify a libtool feature
git checkout upstream git checkout -b mer/libtool
apply hunks
git commit -am"libtool fixes"
Identify an obs-fix feature
git checkout upstream git checkout -b mer/obs-fix
apply hunks
git commit -am"obs pthread fixes"
Now any debian/ hunks
git checkout Mer
apply hunks
git commit -am"Added Mer debianisation"
Now pull it all together
git checkout master
look for all the mer/* and patch/* branches and merge them
git branch -l git merge mer/libtool git merge mer/obs-fix
now use git log to create a top level ChangeLog entry
git add ChangeLog git commit -m"$TAG"
Mark an 'upstream' release
git tag $TAG
Now make a distro release
git checkout Mer git merge master
now use git log to create a debian/changelog entry
git add debian/changelog git commit -m"Mer_$TAG" git tag Mer_$TAG
Verify
Remove all obs code:
cd .. rm $PKG*
regenerate it:
cd $PKG pristine-tar checkout ../$TARBALL debuild -S -i.git
Build or examine to verify
Push
Now push to gitorious
git symbolic-ref HEAD refs/heads/Mer
Logon to http://gitorious.org/mer and create gitorious project
git remote add origin git@gitorious.org:mer/$GPKG.git git push --mirror origin
on gitorious goto 'Edit Repository' and set default to Mer
Handling new upstream
tba
nb push --tags
Working from Gitorious
This should be written to say "Clone this repository on gitorious" and then publish back there and then submit a pull request to Mer.
For core work:
Essentially
git clone git@gitorious.org:mer/$GPKG.git git checkout --track origin/Mer
determine which feature or branch needs work. Then:
git checkout --track origin/mer/<feature>
hack...
Ready to test? You need to make a local test branch based on Mer
git checkout Mer git checkout -b local git merge mer/<feature>
Build and test...
If this works OK then clean up your mer/<feature> branch... probably doing a --squash and push the branch to gitorious.